2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
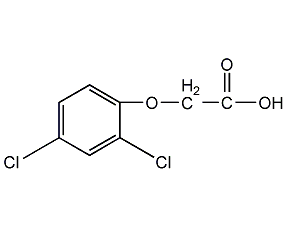
Structural formula
| Business number | 0285 |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C8H6Cl2O3 |
| Molecular weight | 221.04 |
| label |
2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid, (2,4-Dichlorophenoxy)acetic acid, Two to four drops of 2,4-D acid, (2,4-dichlorophenoxy)-Acetic acid, herbicide |
Numbering system
CAS number:94-75-7
MDL number:MFCD00004300
EINECS number:202-361-1
RTECS number:AG6825000
BRN number:1214242
PubChem number:24868891
Physical property data
1. Properties: White to yellow, crystal powder, odorless, industrial product with slight phenol smell.
2. Density (g/mL, 20℃): 1.563
3. Relative vapor density (g/mL, air=1): 7.63
4. Melting point (ºC): 138
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): Undetermined
6. Boiling point (ºC, 0.05KPa): 160
7. Refractive index: Undetermined
8. Flash point (ºC): Undetermined
9. Specific rotation (º): Undetermined
10. Autoignition point or ignition temperature (ºC): Undetermined
11. Vapor pressure (mmHg, ºC): Undetermined
12. Saturated vapor pressure (kPa, 160ºC ): 0.053
13. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol): Undetermined
14. Critical temperature (ºC): Undetermined
15. Critical pressure (KPa): Undetermined
16. Log value of oil-water (octanol/water) partition coefficient: Undetermined
17. Explosion upper limit (%, V/V): Undetermined Determined
18. Lower explosion limit (%, V/V): Undetermined
19. Solubility: Slightly soluble in water, slightly soluble in oil, soluble in ethanol, etc.
Toxicological data
1. Acute toxicity: Rat oral LD50: 666-1313mg/kg
Mouse oral LD5O: 375mg/kg
Rat dermal LD5O: 1500mg/ kg
Ecological data
Slightly harmful to water.
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 48.91
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 148.4
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 397.2
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 51.2
5. Polarizability (10-24cm3): 19.39
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 1
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 3
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 3
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 46.5
7.Number of heavy atoms: 13
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 186
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 0
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
Avoid contact with oxides and alkalis.
Storage method
Store in a cool, ventilated warehouse. Keep away from fire and heat sources. They should be stored separately from oxidants, alkalis, and food chemicals, and avoid mixed storage. Equipped with the appropriate variety and quantity of fire equipment. Suitable materials should be available in the storage area to contain spills.
Synthesis method
1. First chlorine phenol to prepare 2,4-dichlorophenol. The latter is condensed with chloroacetic acid in the presence of sodium hydroxide to form 2,4-D sodium salt, which is then acidified to form 2,4-D original salt. medicine. Another new process is obtained by condensing phenol and chloroacetic acid under alkaline conditions and then chlorinating it.
2. 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid sodium is prepared by heating and refluxing 2,4-dichlorophenol and monochloroacetic acid in NaOH solution, and then acidifying it with hydrochloric acid.
3. Using phenol as raw material, the product can be obtained by first condensation with chloroacetic acid and then chlorination, or by first chlorination and then condensation with chloroacetic acid. (1) Condensation first and then chlorination process. Place the phenol in the reaction kettle, heat and melt it, add 2.2 times (molar ratio) of sodium hydroxide and 1.2 times (molar ratio) of chloroacetic acid, and react at 100-110°C for 30 minutes. After the reactants are cooled and neutralized with hydrochloric acid, phenoxyacetic acid can be precipitated with a yield of more than 82%.
Phenoxyacetic acid is slowly introduced into 1.4-1.6 times (molar ratio) of chlorine gas at 65-90°C, and the chlorination product is 2,4-difluorophenoxyacetic acid, with a yield of 89%.
(2) Chlorination first and then condensation process. Place the molten phenol in a chlorinator and pass chlorine at 45-65°C for about 8-9 hours. The chlorination reaction ends when the relative density of the reaction material reaches 1.406 (40°C). Add 30% sodium hydroxide solution to the reactant while it is hot. After heating to boiling, add sodium chloroacetate solution dropwise and reflux for 4-5 hours. After cooling slightly, neutralize to pH 1-3 with 30% hydrochloric acid. Add benzene to extract while hot, and separate the organic layer. After cooling, white crystals precipitate, and the finished product is obtained through suction filtration and drying.
4. Using phenol as raw material, the product can be obtained by first condensation with chloroacetic acid and then chlorination, or by first chlorination and then condensation with chloroacetic acid.
Condensation first and then chlorination process
Place phenol in the reactor, heat and melt, add 2.2 times (molar ratio) of sodium hydroxide and 1.2 times (molar ratio) of chloroacetic acid, and React at 100~110°C for 30 minutes. After the reactants are cooled and neutralized with hydrochloric acid, phenoxyacetic acid can be precipitated with a yield of more than 82%.
Phenoxyacetic acid is slowly passed into 1.4 to 1.6 times (molar ratio) of chlorine at 65~90°C. The chlorination product is 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid, with a yield of 89%.
Chlorination first and then condensation process
Place the molten phenol in a chlorinator and pass chlorine at 45-65°C for about 8-9 hours. When the relative density of the reaction material reaches 1.406 (40°C) The chlorination reaction is completed. Add 30% sodium hydroxide solution to the reactant while it is hot. After heating to boiling, add sodium chloroacetate solution dropwise and reflux for 4 to 5 hours. After cooling slightly, neutralize with 30% hydrochloric acid to a Ph value of 1 to 3. Add benzene to extract while hot, and separate the organic layer. After cooling, white crystals precipitate, and the finished product is obtained by suction filtration and drying.
Purpose
It is used as a herbicide and plant growth agent in agriculture, and is often processed into sodium salt, ammonium salt or ester liquids, powders, emulsions, ointments, etc.
extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/44066
extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/1015
extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/category/products/page/5
extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/07/123-1.jpg
extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/44258
extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/1891
extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/1824
extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2020/06/75.jpg
extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/40230
extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/cas-1067-33-0-3/


